Verbs are the backbone of English sentences because they show action or state of being. Among the different kinds of verbs, finite and non-finite verbs often confuse students. Finite verbs change according to the subject and tense, while non-finite verbs do not change and are usually used with other verbs. Understanding the difference between finite and non-finite verbs helps learners form correct sentences and improve their grammar skills. In this article, you will learn this difference in easy English with clear explanations and simple examples that make the concept easy to understand and apply in daily writing and speaking.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat Are Finite Verbs in English?
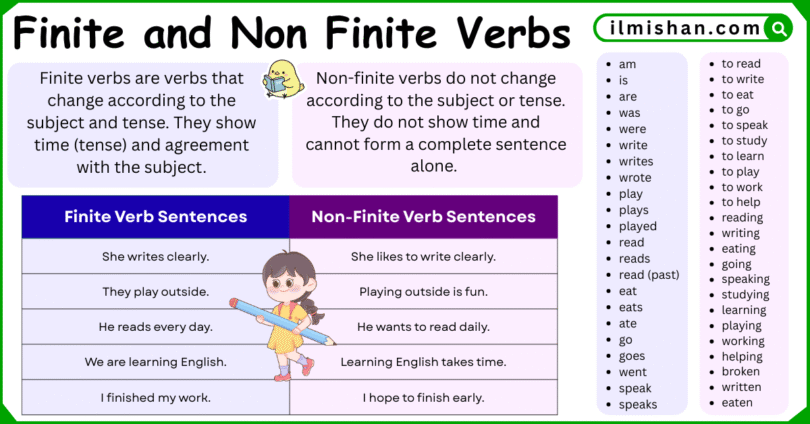
Finite verbs are verbs that change according to the subject and tense. They show time (tense) and agreement with the subject. A sentence cannot be complete without a finite verb.
Finite verbs clearly indicate:
- Who is doing the action
- When the action happens
They are the main verbs of independent clauses.
Examples:
- She writes neatly.
- They are playing outside.
- He was reading a book.
In each sentence, the verb changes with the subject or tense, which makes it finite.
Key Features of Finite Verbs
- Show tense (present, past, future)
- Change according to subject (singular/plural)
- Can form a complete sentence
- Act as the main verb in a clause
What Are Non-Finite Verbs in English?
Non-finite verbs do not change according to the subject or tense. They do not show time and cannot form a complete sentence alone. They are used to add more information to a sentence.
Non-finite verbs often act as:
- Nouns
- Adjectives
- Adverbs
They usually appear in verb phrases or dependent clauses.
Examples:
- I like to read books.
- Running is good exercise.
- The boy playing outside is my cousin.
Here, the verbs to read, running, and playing do not show tense or subject agreement.
Main Types of Non-Finite Verb
Non-finite verbs appear in three common forms.
Infinitives
Infinitives are usually formed with to + base verb. They often express purpose, intention, or desire.
Examples:
- She wants to learn English.
- He came to help me.
Gerunds
Gerunds are verbs ending in -ing that function as nouns.
Examples:
- Swimming is fun.
- I enjoy reading novels.
Participles
Participles act like adjectives and describe nouns.
They can be present participles (-ing) or past participles (-ed / third form).
Examples:
- The crying baby is hungry.
- The broken chair is useless.
Finite vs Non-Finite Verb: Clear Comparison
| Finite Verb | Non-Finite Verb |
|---|---|
| Show tense | Do not show tense |
| Change with subject | Do not change with subject |
| Can complete a sentence | Cannot complete a sentence alone |
| Act as main verbs | Act as nouns, adjectives, or adverbs |
| Used in independent clauses | Used in dependent structures |
How to Identify Finite and Non-Finite Verb
A simple method helps learners identify them easily.
Check for Tense
- If the verb shows time, it is finite.
- If it does not show time, it is non-finite.
Check for Sentence Completion
- If the sentence feels complete, the verb is finite.
- If the sentence feels incomplete, the verb is non-finite.
Example:
- She likes tea. (finite)
- She likes to drink tea. (non-finite)
Use of Finite and Non Finite Verb Together
In many sentences, both verb types appear together.
Examples:
- He decided (finite) to leave (non-finite) early.
- She is (finite) studying (non-finite) English.
This combination is common in complex sentences.
Why This Topic Is Important for Exams
Finite and non-finite verbs are tested in:
- Sentence transformation
- Error correction
- Identifying clauses
- Grammar MCQs
Understanding this topic helps students:
- Write grammatically correct sentences
- Analyze sentence structure clearly
- Improve writing and speaking accuracy
Common Mistakes ESL Learners Make
- Treating non-finite verbs as main verbs
- Forgetting tense agreement in finite verbs
- Confusing gerunds with present participles
- Using infinitives incorrectly after verbs
Regular practice reduces these errors.
Quick Tips for Easy Learning
- Every complete sentence needs one finite verb
- Non-finite verbs add meaning, but cannot stand alone
- Look for tense and subject agreement
- Practice identifying verb forms in sentences
Example of Finite Verbs vs Non Finite Verb
| Finite Verb Sentences | Non-Finite Verb Sentences |
|---|---|
| She writes clearly. | She likes to write clearly. |
| They play outside. | Playing outside is fun. |
| He reads every day. | He wants to read daily. |
| We are learning English. | Learning English takes time. |
| I finished my work. | I hope to finish early. |
| She is cooking dinner. | She went to cook dinner. |
| They won the match. | They were happy to win. |
| He opened the door. | He tried to open the door. |
| We watch movies. | We enjoy watching movies. |
| I am studying now. | Studying now is important. |
| She teaches English. | She loves to teach children. |
| They are waiting here. | They stopped to wait here. |
| He fixed the chair. | He learned to fix chairs. |
| We walk together. | We went to walk together. |
| I understand the rule. | I tried to understand it. |
| She answered politely. | She forgot to answer earlier. |
| They are building a house. | They plan to build a house. |
| He lost the key. | He searched to find it. |
| We completed the task. | We were glad to complete it. |
| I remember her name. | I struggle to remember names. |
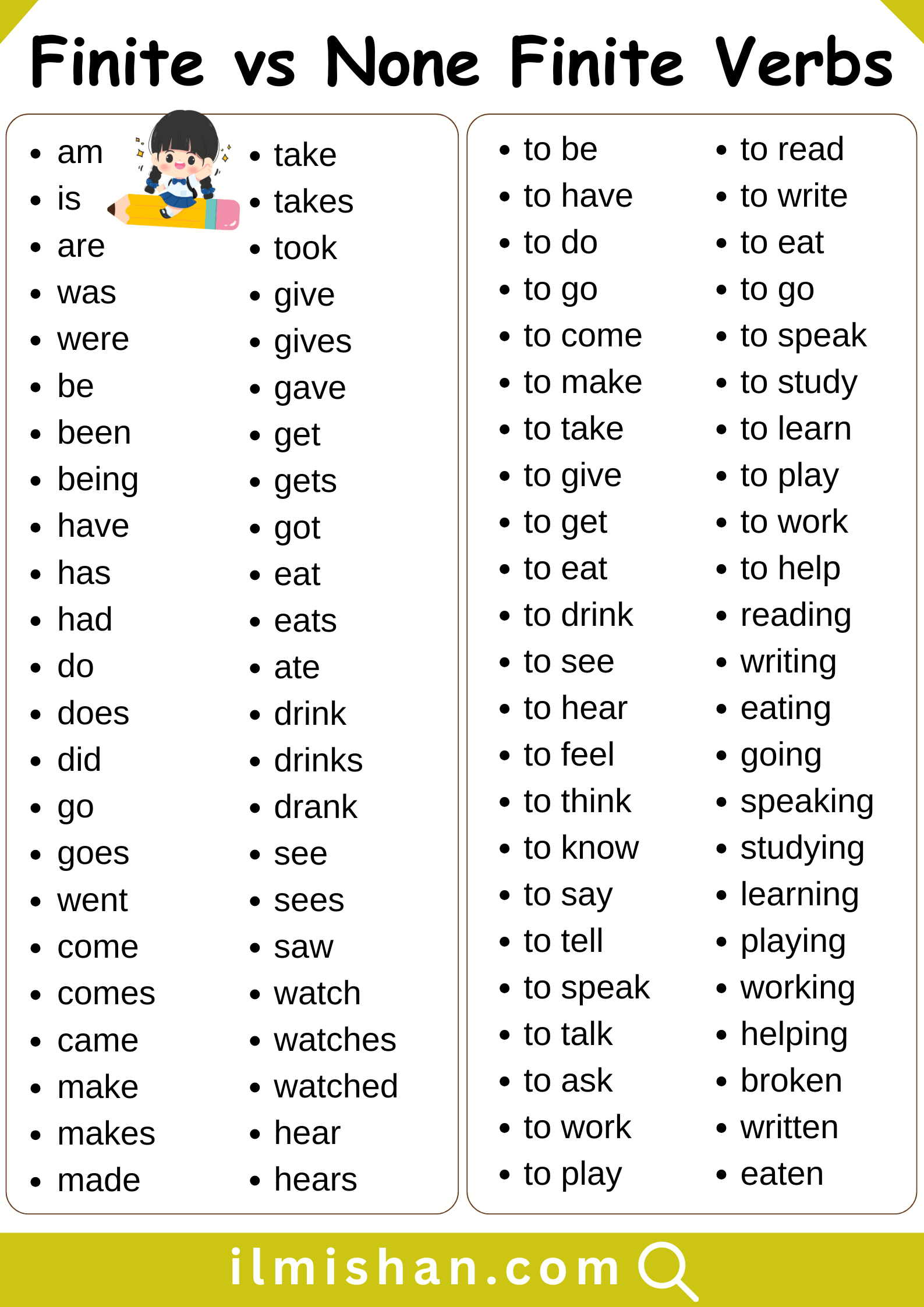
List of Finite and non Finite Verb
- am
- is
- are
- was
- were
- write
- writes
- wrote
- play
- plays
- played
- read
- reads
- read (past)
- eat
- eats
- ate
- go
- goes
- went
- speak
- speaks
- spoke
- study
- studies
- studied
- run
- runs
- ran
- finish
List of Non Finite Verb
- to read
- to write
- to eat
- to go
- to speak
- to study
- to learn
- to play
- to work
- to help
- reading
- writing
- eating
- going
- speaking
- studying
- learning
- playing
- working
- helping
- broken
- written
- eaten
- gone
- spoken
- studied
- taken
- seen
- done
- built
Learn more helpful articles