Understanding the difference between gerunds and infinitives is an important part of learning English grammar. Both forms are made from verbs, but they are used in different ways in a sentence. A gerund is a verb that ends in -ing and works like a noun, while an infinitive usually begins with to and keeps the base form of the verb. Many students feel confused about when to use each form, especially after certain verbs. In this article, you will learn Difference Between Gerunds and infinitives definition with Example, making it easier to understand their differences and use them correctly in everyday sentences.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat Are Gerunds?
A gerund is a verb ending in -ing that is used as a noun. It names an activity instead of showing an action. For example, when you say “Reading helps me relax,” the word reading acts like a thing you are talking about. Gerunds make it easy to describe everyday actions in a simple way, and they fit naturally in sentences as the subject or object.
You can use gerunds as:
- the subject of a sentence
- the object of a verb
- the object of a preposition
Examples:
- Swimming is good exercise.
- She enjoys reading.
- They left without saying goodbye.
Here, swimming, reading, and saying act like nouns even though they come from verbs.
What Are Infinitives?
An infinitive is the base form of a verb usually written with the word to in front of it, like to eat, to walk, or to learn. It does not show time or action by itself; instead, it names a purpose, a plan, or a reason. For example, in the sentence “I want to rest,” the phrase to rest tells what the person wants to do. Infinitives are simple, flexible, and fit naturally in many sentences to explain goals or intentions.
Examples:
- I want to learn English.
- They decided to leave early.
- She has a plan to study abroad.
Here, to learn, to leave, and to study act as the purpose or intention.
Gerunds and infinitives: Basic Difference
Both gerunds and infinitives can act like nouns, but they are not used in the same situations.
- Use gerunds for real, general, or completed actions.
- Use infinitives for future actions, intentions, or specific goals.
Examples:
- I stopped smoking. (I quit the habit.)
- I stopped to smoke. (I stopped something so that I could smoke.)
Key Differences in a Table
Gerunds and Infinitives Comparison Table
| Feature | Gerund (-ing form) | Infinitive (to + verb) |
|---|---|---|
| Form | verb + ing | to + base verb |
| Function | acts like a noun | acts like a noun, adjective, or adverb |
| Use | general actions, hobbies, completed actions | future actions, intentions, purposes |
| Example | She likes cooking. | She wants to cook. |
When to Use Gerunds
Some verbs are always followed by a gerund. These verbs talk about likes, dislikes, and activities.
Common Verbs Followed by Gerunds
| Verb | Example |
|---|---|
| enjoy | I enjoy reading. |
| avoid | She avoids driving at night. |
| consider | They are considering moving. |
| finish | He finished writing his report. |
| suggest | She suggested meeting earlier. |
When to Use Infinitives
Some verbs are always followed by an infinitive. These verbs usually express desire, plan, attempt, or decision.
Common Verbs Followed by Infinitives
Verbs That Can Take Both (But With a Change in Meaning)
Some verbs can follow either a gerund or an infinitive, but the meaning changes.
Meaning Change Table
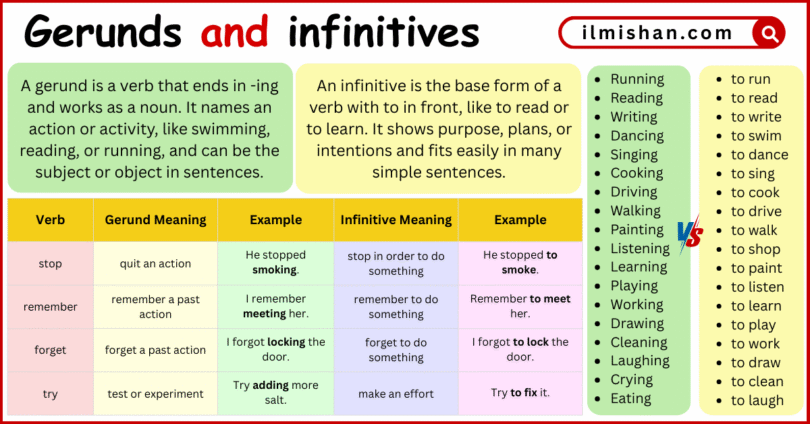
| Verb | Gerund Meaning | Example | Infinitive Meaning | Example |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| stop | quit an action | He stopped smoking. | stop in order to do something | He stopped to smoke. |
| remember | remember a past action | I remember meeting her. | remember to do something | Remember to meet her. |
| forget | forget a past action | I forgot locking the door. | forget to do something | I forgot to lock the door. |
| try | test or experiment | Try adding more salt. | make an effort | Try to fix it. |
Gerunds After Prepositions
Gerunds always follow prepositions.
Examples:
- She is good at painting.
- He left without saying anything.
- They are interested in learning Spanish.
You never use an infinitive after a preposition.
❌ good at to paint
✔️ good at painting
Infinitives to Show Purpose
Infinitives often express the reason for an action.
Examples:
- She came to study.
- He exercises to stay healthy.
- They opened the window to get fresh air.
Gerunds as Subjects and Objects
Gerunds as subjects:
- Eating vegetables is healthy.
- Walking every day improves fitness.
Gerunds as objects:
- She enjoys cooking.
- I love dancing.
Infinitives as Subjects and Objects
Infinitives as subjects:
- To learn a new language is exciting.
- To travel the world is my dream.
Infinitives as objects:
- He promised to help.
- They hope to win.
Common Mistakes and How to Fix Them
Mistake 1: Using Infinitive After Prepositions
❌ She is interested to learn English.
✔️ She is interested in learning English.
Mistake 2: Using Gerund After Certain Verbs
❌ I want going home.
✔️ I want to go home.
Mistake 3: Confusing Meaning-Change Verbs
❌ I stopped to smoke. (Incorrect if you quit smoking.)
✔️ I stopped smoking. (Correct.)
Advanced Rules of Gerunds and infinitives
1. Some Verbs Need an Object + Infinitive
Examples:
- She told me to wait.
- They asked him to help.
2. Some Verbs Need an Object + Gerund
Examples:
- I appreciate you coming early.
- She dislikes him interrupting.
3. Infinitives After Adjectives
Examples:
- It is easy to learn.
- I am happy to help.
- This book is hard to read.
Gerunds and infinitives Examples in English
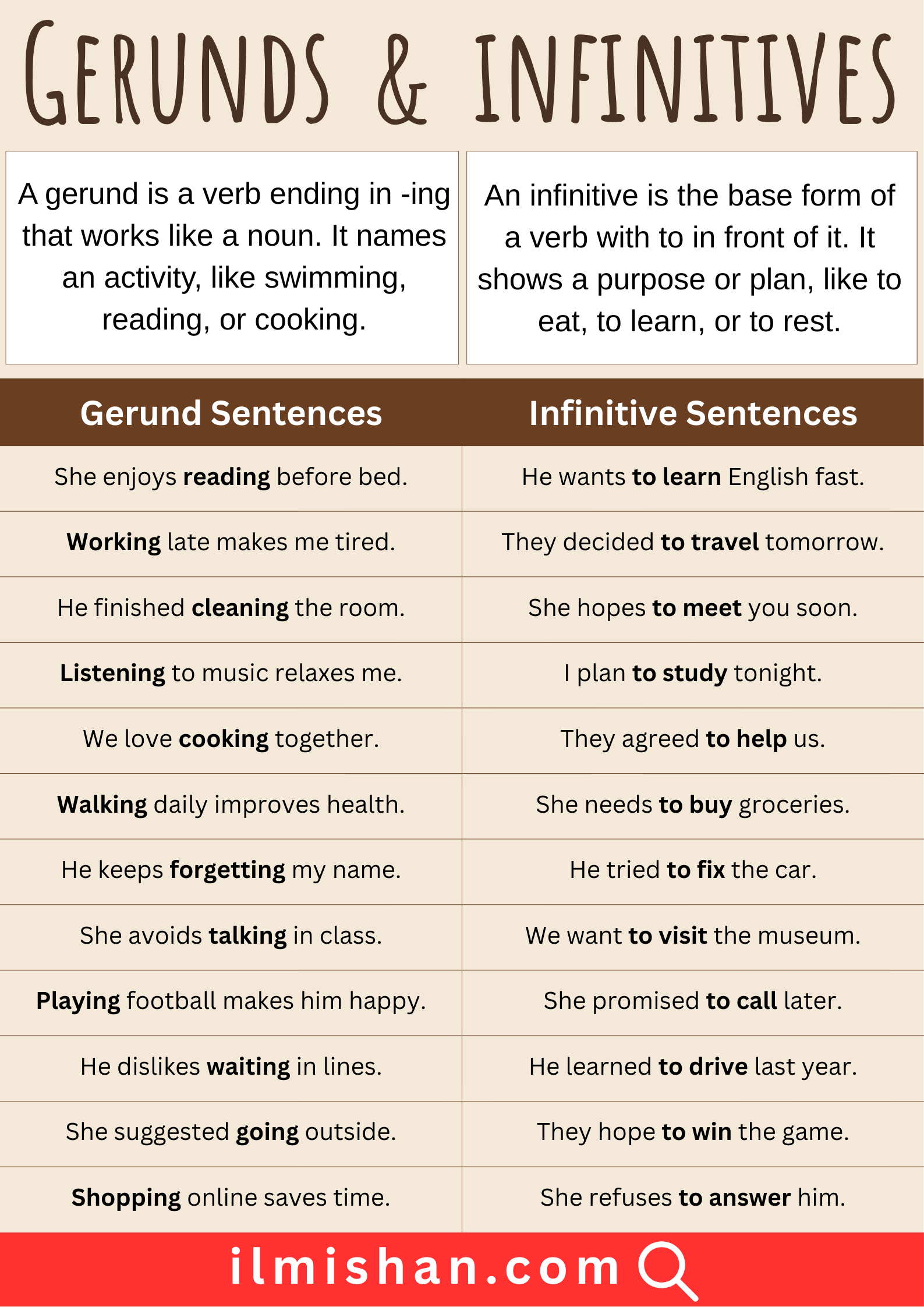
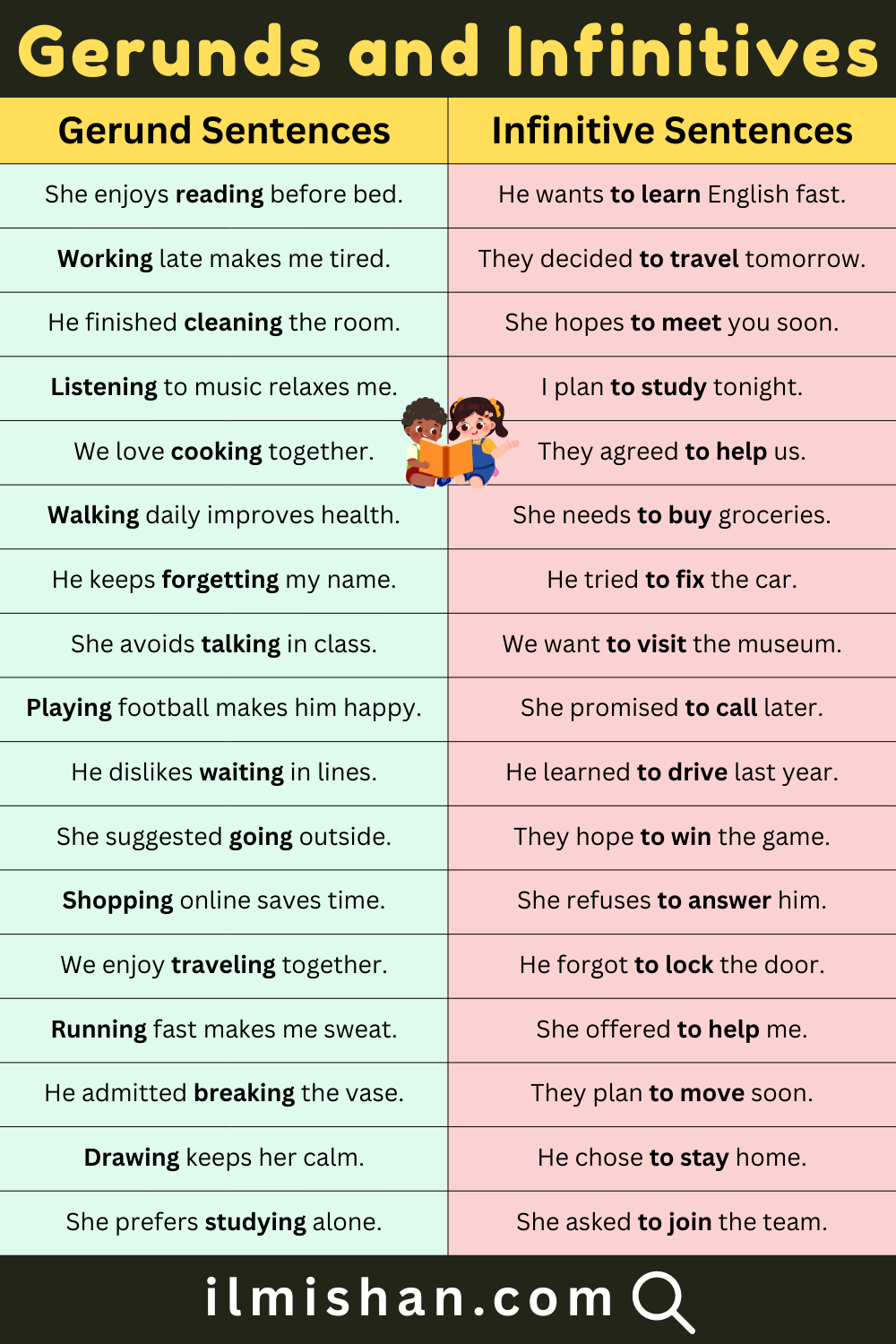
| Gerund Sentences | Infinitive Sentences |
|---|---|
| She enjoys reading before bed. | He wants to learn English fast. |
| Working late makes me tired. | They decided to travel tomorrow. |
| He finished cleaning the room. | She hopes to meet you soon. |
| Listening to music relaxes me. | I plan to study tonight. |
| We love cooking together. | They agreed to help us. |
| Walking daily improves health. | She needs to buy groceries. |
| He keeps forgetting my name. | He tried to fix the car. |
| She avoids talking in class. | We want to visit the museum. |
| Playing football makes him happy. | She promised to call later. |
| He dislikes waiting in lines. | He learned to drive last year. |
| She suggested going outside. | They hope to win the game. |
| Shopping online saves time. | She refuses to answer him. |
| We enjoy traveling together. | He forgot to lock the door. |
| Running fast makes me sweat. | She offered to help me. |
| He admitted breaking the vase. | They plan to move soon. |
| Drawing keeps her calm. | He chose to stay home. |
| She prefers studying alone. | She asked to join the team. |
| Swimming improves stamina. | He hopes to grow his business. |
| They practice speaking English. | She needs to rest a little. |
| Laughing together builds friendships. | They want to start early. |
List of Gerunds and infinitives in English
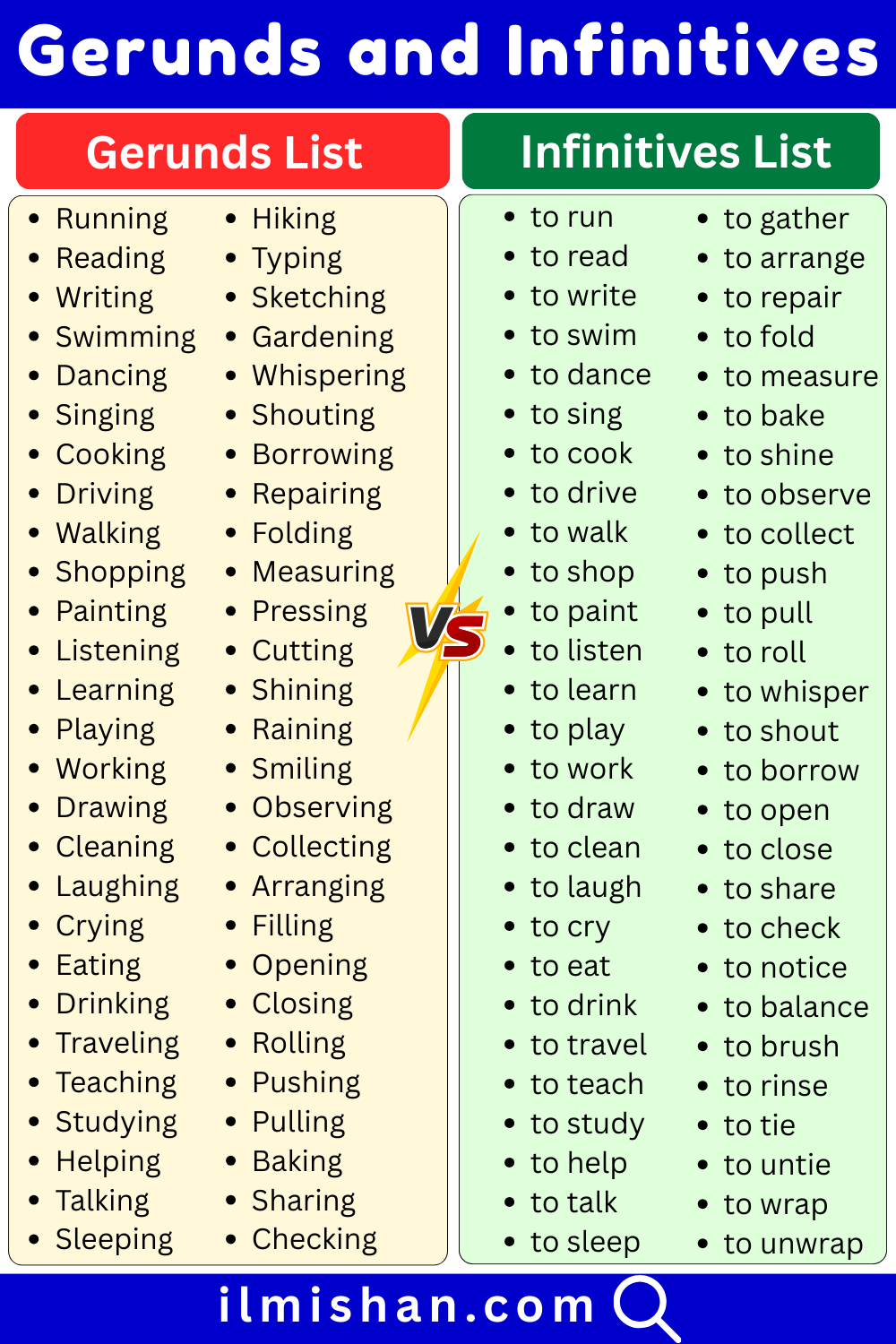
List of Gerunds
- Running
- Reading
- Writing
- Swimming
- Dancing
- Singing
- Cooking
- Driving
- Walking
- Shopping
- Painting
- Listening
- Learning
- Playing
- Working
- Drawing
- Cleaning
- Laughing
- Crying
- Eating
- Drinking
- Traveling
- Teaching
- Studying
- Helping
- Talking
- Sleeping
- Jogging
- Climbing
- Practicing
List of Infinitives in English
- to run
- to read
- to write
- to swim
- to dance
- to sing
- to cook
- to drive
- to walk
- to shop
- to paint
- to listen
- to learn
- to play
- to work
- to draw
- to clean
- to laugh
- to cry
- to eat
- to drink
- to travel
- to teach
- to study
- to help
- to talk
- to sleep
- to jog
- to climb
- to practice
Learn more helpful articles