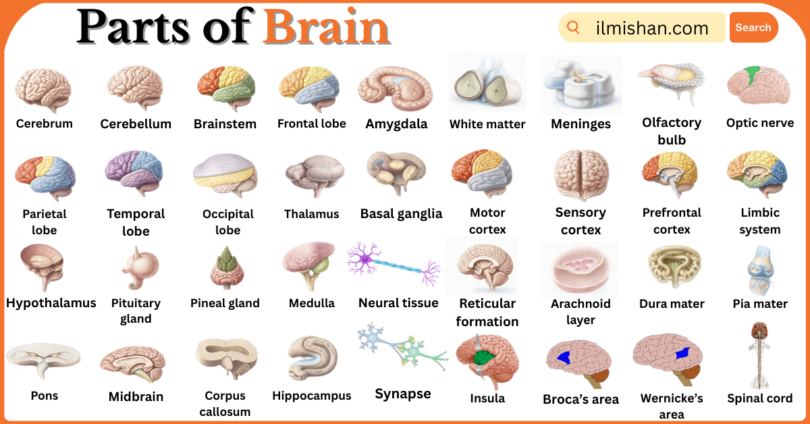
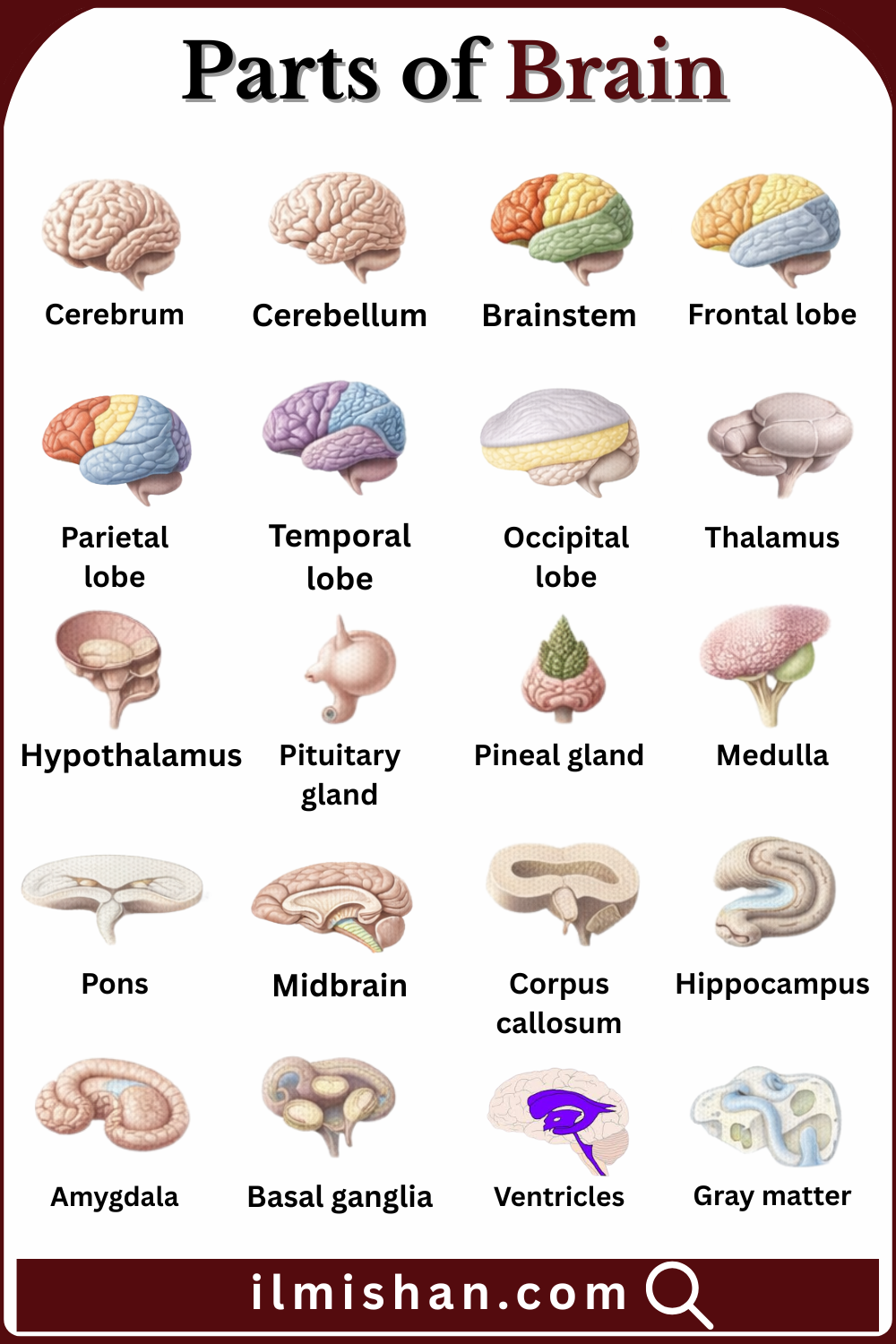
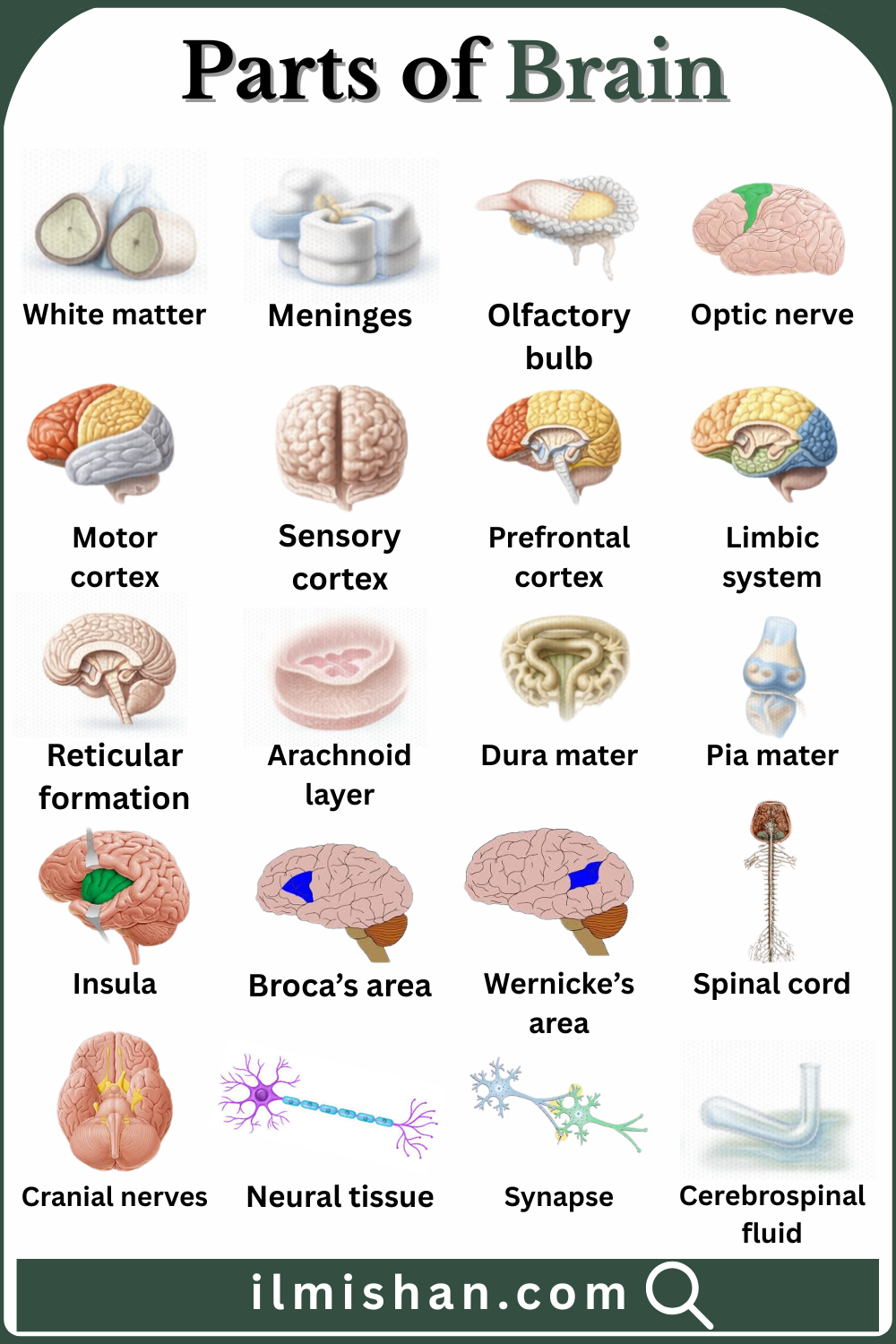
The brain is the main control center of the human body, responsible for thinking, memory, movement, and emotions. It sends and receives signals that help the body work properly. The brain is made up of different parts, and each part has a special function, such as controlling balance, breathing, or decision-making. Understanding the parts of the brain helps us learn how our body and mind work together. In this article, you will learn Parts of Brain with Names in English with Pictures, explained in easy and simple language for clear understanding.
Table of Contents
ToggleParts of Brain with Names list
- Cerebrum
- Cerebellum
- Brainstem
- Frontal lobe
- Parietal lobe
- Temporal lobe
- Occipital lobe
- Thalamus
- Hypothalamus
- Pituitary gland
- Pineal gland
- Medulla
- Pons
- Midbrain
- Corpus callosum
- Hippocampus
- Amygdala
- Basal ganglia
- Ventricles
- Gray matter
Common Parts of Brain with their Names and Pictures
- Cerebrum
The largest part of the brain, responsible for thinking, learning, memory, emotions, speech, and voluntary muscle movements that control daily activities.
- Cerebellum
The part of the brain that controls balance, posture, coordination, and smooth movement, helping the body perform precise and controlled actions.
- Brainstem
The lower part of the brain connecting to the spinal cord, controlling breathing, heartbeat, swallowing, and other vital life-support functions.
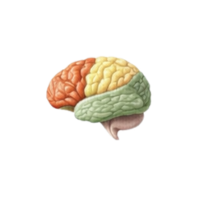
- Frontal lobe
The front region of the cerebrum involved in decision-making, problem-solving, personality, emotions, speech, and voluntary motor control.
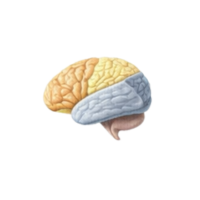
- Parietal lobe
The brain region that processes touch, temperature, pain, and spatial awareness, helping understand body position and sensory information.
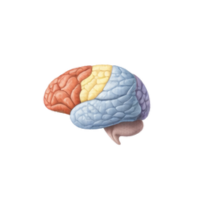
- Temporal lobe
The side region of the brain responsible for hearing, language understanding, memory formation, and emotional responses.
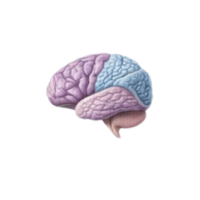
- Occipital lobe
The back part of the brain that processes visual information, including color, shape, and movement from the eyes.
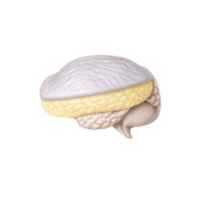
- Thalamus
A relay center that sends sensory signals to appropriate brain areas and helps regulate consciousness and alertness.
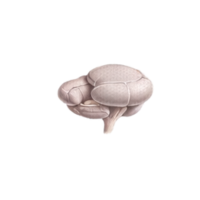
- Hypothalamus
A small but vital brain part that controls hunger, thirst, body temperature, hormones, and links the nervous system to the endocrine system.
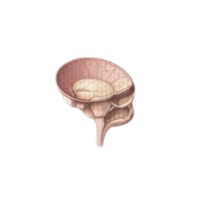
- Pituitary gland
A small gland that releases hormones controlling growth, metabolism, reproduction, and other endocrine glands in the body.

- Pineal gland
A tiny gland that produces melatonin, regulating sleep-wake cycles and biological rhythms.

- Medulla
The lower part of the brainstem that controls breathing, heart rate, blood pressure, and reflexes like coughing and swallowing.

- Pons
A brainstem structure that connects different brain parts and helps regulate breathing, sleep, and facial movements.

- Midbrain
The upper part of the brainstem involved in vision, hearing, eye movement, and body motion control.
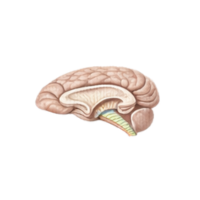
- Corpus callosum
A thick band of nerve fibers connecting the left and right hemispheres, allowing communication between both sides of the brain.

- Hippocampus
A brain structure essential for learning, memory formation, and storing long-term information.

- Amygdala
A small structure that processes emotions such as fear, anger, pleasure, and emotional memories.
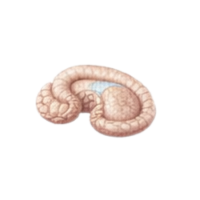
- Basal ganglia
A group of structures that help control movement, muscle coordination, and habit formation.
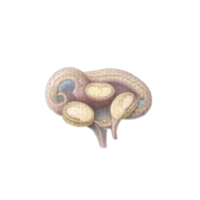
- Ventricles
Fluid-filled cavities in the brain that contain cerebrospinal fluid, cushioning the brain and maintaining internal pressure.
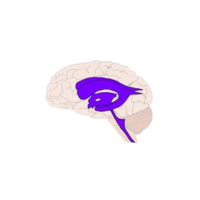
- Gray matter
Brain tissue made of neuron cell bodies, responsible for processing information, thinking, and decision-making.

Common Brain parts and Name
- White matter
- Meninges
- Cerebrospinal fluid
- Olfactory bulb
- Optic nerve
- Motor cortex
- Sensory cortex
- Prefrontal cortex
- Limbic system
- Reticular formation
- Arachnoid layer
- Dura mater
- Pia mater
- Insula
- Broca’s area
- Wernicke’s area
- Spinal cord
- Cranial nerves
- Neural tissue
- Synapse
Explore Brain Parts with Names and images
- White matter
Brain tissue made of nerve fibers that transmit signals between different brain regions, enabling fast communication and coordination of activities.

- Meninges
Protective membranes covering the brain and spinal cord, providing support, protection, and cushioning against physical injury.

- Cerebrospinal fluid
Clear fluid surrounding the brain and spinal cord that cushions them, removes waste, and helps maintain stable pressure inside the skull.

- Olfactory bulb
A brain structure that receives smell signals from the nose and sends them to areas responsible for odor recognition.
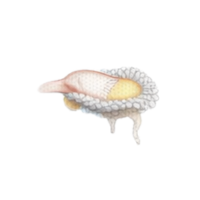
- Optic nerve
The nerve that carries visual information from the eyes to the brain for sight and image processing.

- Motor cortex
A region of the frontal lobe that controls voluntary muscle movements and body actions.
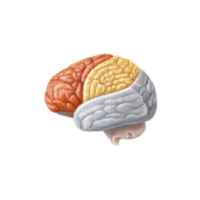
- Sensory cortex
The brain area that receives and interprets sensory information such as touch, pain, temperature, and pressure.
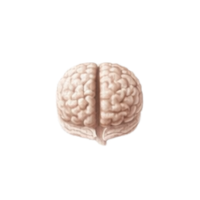
- Prefrontal cortex
The front part of the frontal lobe responsible for planning, decision-making, behavior control, and personality.
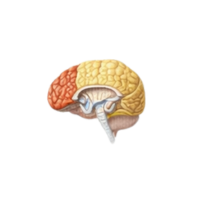
- Limbic system
A group of brain structures involved in emotions, memory, motivation, and emotional behavior.
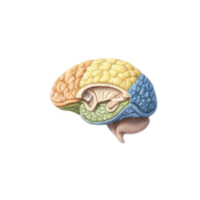
- Reticular formation
A network of neurons that regulates alertness, sleep, attention, and consciousness.
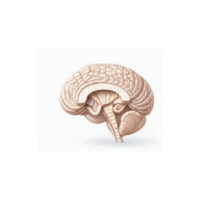
- Arachnoid layer
The middle layer of the meninges that cushions the brain and contains cerebrospinal fluid.

- Dura mater
The tough outer layer of the meninges that provides strong protection to the brain and spinal cord.

- Pia mater
The thin inner layer of the meninges that closely covers the brain and spinal cord surface.

- Insula
A deep brain region involved in emotions, taste, self-awareness, and body sensations.
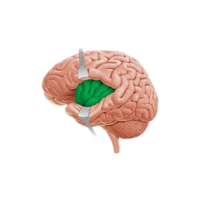
- Broca’s area
A brain region responsible for speech production and language expression.
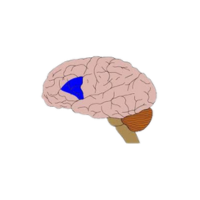
- Wernicke’s area
A brain area involved in understanding spoken and written language.
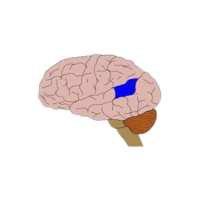
- Spinal cord
A long nerve structure connecting the brain to the body, transmitting signals and controlling reflexes.
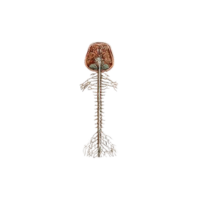
- Cranial nerves
Twelve pairs of nerves that control sensory and motor functions of the head and neck.
- Neural tissue
Specialized tissue made of neurons and support cells that transmit electrical signals in the nervous system.
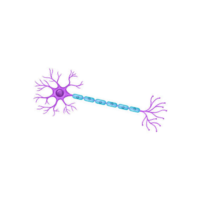
- Synapse
The tiny gap between neurons where nerve signals are transmitted using chemical or electrical signals.