Types of Leaves with Names in English
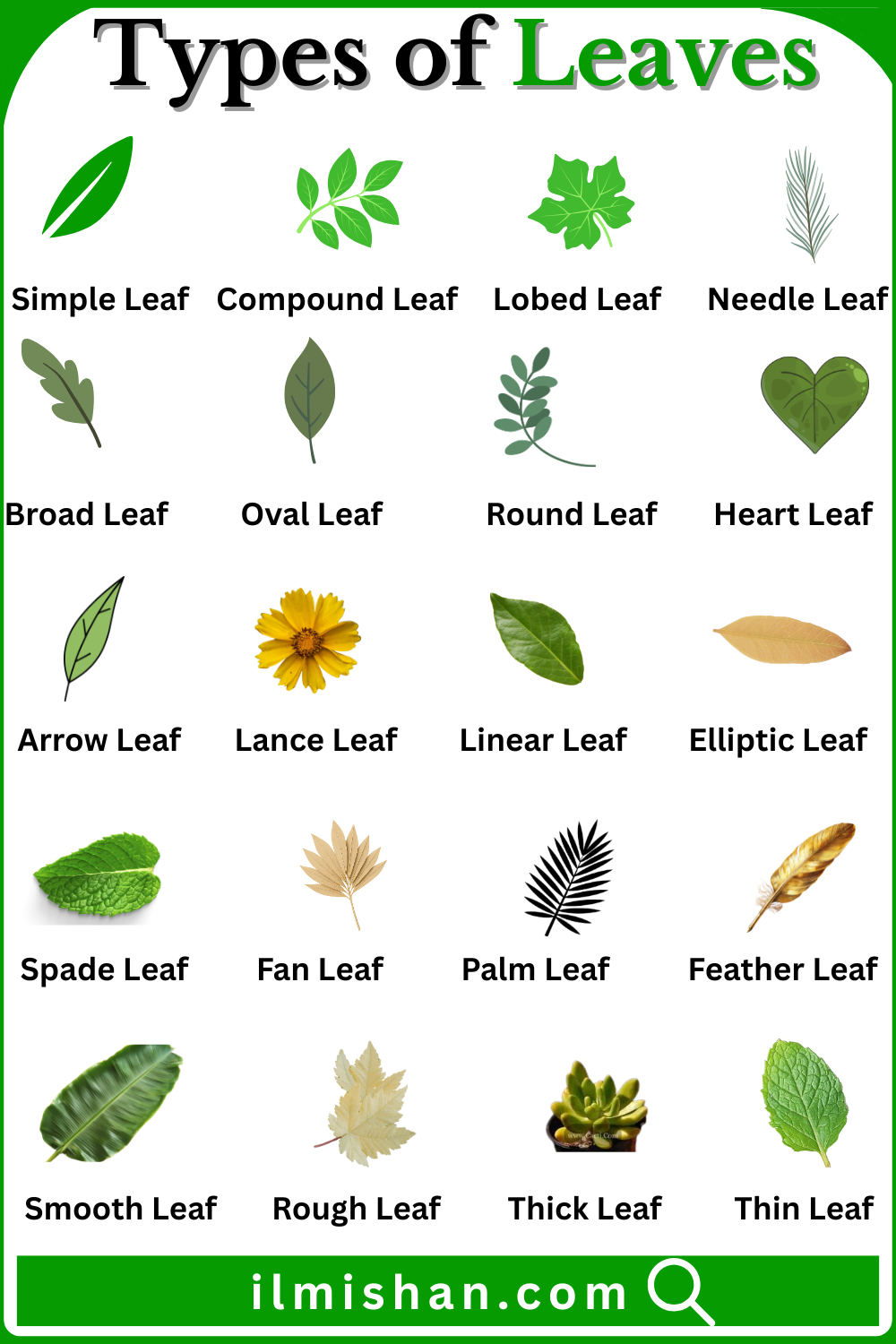
- Simple Leaf
- Compound Leaf
- Lobed Leaf
- Needle Leaf
- Broad Leaf
- Oval Leaf
- Round Leaf
- Lance Leaf
- Linear Leaf
- Elliptic Leaf
- Spade Leaf
- Fan Leaf
- Palm Leaf
- Heart Leaf
- Feather Leaf
- Smooth Leaf
- Arrow Leaf
- Rough Leaf
- Thick Leaf
Types of Leaves with Names and their Pictures
- Simple Leaf
A leaf having a single, whole blade attached to the stem, not divided into smaller parts, common in mango and guava plants, and performing photosynthesis as one complete unit.

- Compound Leaf
A leaf divided into several smaller leaflets attached to one stalk, where each leaflet lacks a bud, commonly seen in neem, rose, and pea plants in many regions.

- Lobed Leaf
A leaf with clear rounded or pointed sections called lobes, cut partly toward the center, but remaining one piece, typical of oak and maple trees.

- Needle Leaf
A long, thin, needle-shaped leaf adapted to cold or dry climates, reducing water loss, mostly found on pine, fir, and other conifer trees worldwide.

- Broad Leaf
A leaf with a wide, flat surface that captures more sunlight, supporting efficient photosynthesis, common in many deciduous plants growing in warm or moderate climates.

- Oval Leaf
A leaf shaped like an egg, wider at the middle and narrower at both ends, commonly found in tea, basil, and many garden plants.

- Round Leaf
A leaf that is almost circular in shape with smooth edges, often seen in water plants and ground herbs, allowing even light absorption across the surface.

- Lance Leaf
A long, narrow leaf tapering toward both ends, resembling a lance, common in grasses and medicinal plants, helping reduce wind resistance in open habitats.

- Linear Leaf
A very narrow leaf with nearly parallel sides throughout its length, typical of grasses and cereals, helping minimize water loss and withstand strong winds.

- Elliptic Leaf
A leaf shaped like an ellipse, widest at the center and evenly narrowing at both ends, common in shrubs and trees with balanced sunlight capture.

- Spade Leaf
A leaf shaped like a spade symbol, broad at the base and pointed at the tip, found in some ornamental and wild plants in specific regions.

- Fan Leaf
A leaf spreading outward in a fan-like form from one point, best known in ginkgo, helping collect sunlight efficiently from different directions.

- Palm Leaf
A large leaf divided into sections that radiate from a central point like fingers, typical of coconut and date palms in tropical regions.

- Heart Leaf
A leaf shaped like a heart with a visible notch at the base, common in betel, peepal, and many climbing plants.

- Feather Leaf
A leaf divided into many small leaflets arranged along both sides of a central stalk, resembling a feather, common in neem and rose plants.

- Smooth Leaf
A leaf with an even surface lacking hairs or rough texture, allowing water to flow easily and reducing dust buildup during rainfall.

- Arrow Leaf
A leaf shaped like an arrowhead with pointed side lobes at the base, commonly found in aquatic and marsh plants growing in wetlands.

- Rough Leaf
A leaf with a coarse, uneven surface often due to tiny hairs, helping protect the plant from insects and grazing animals.

- Thick Leaf
A leaf with fleshy, dense tissues that store water, adapted to dry conditions, commonly seen in succulent plants like aloe.

List of Leaves Name in English
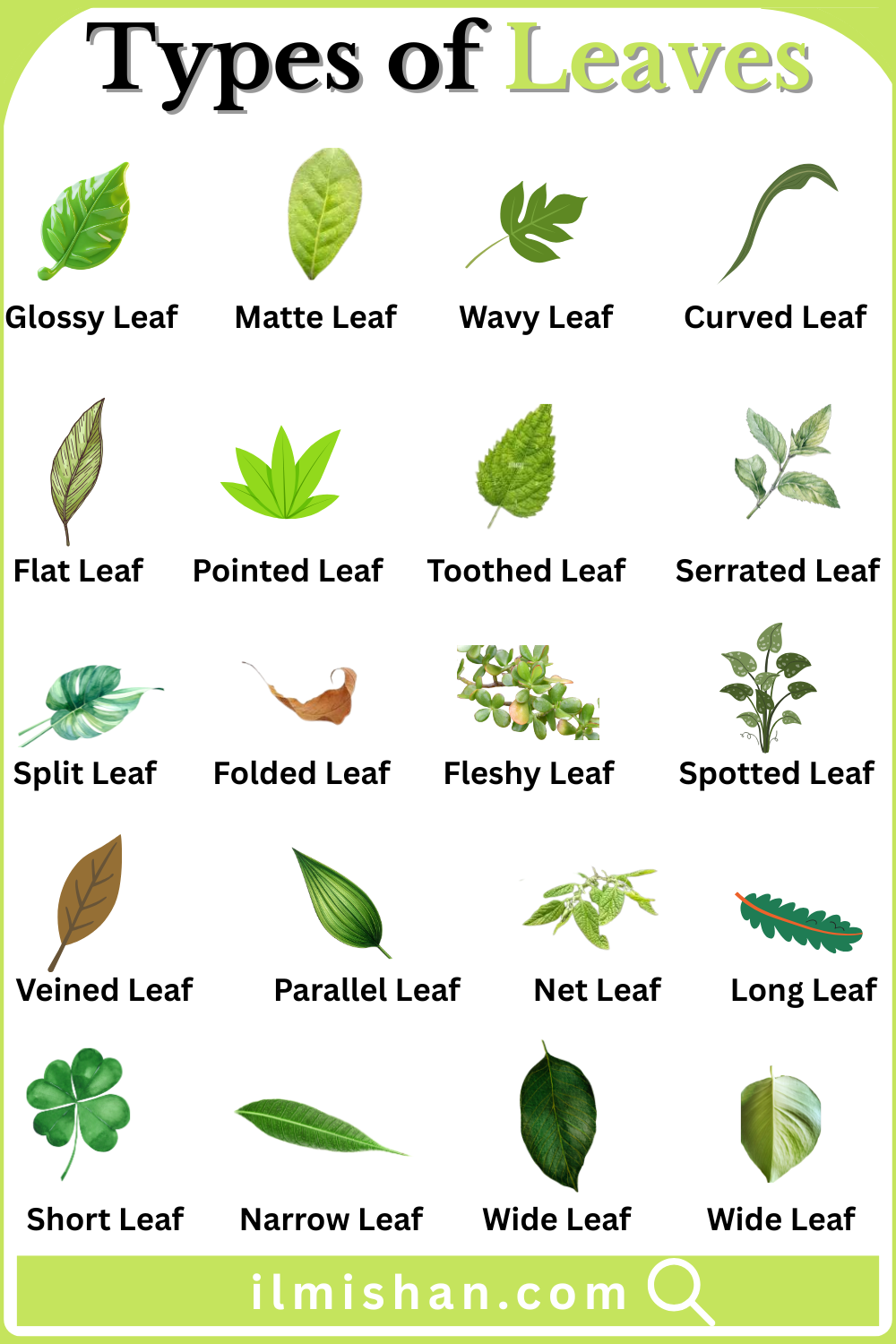
- Glossy Leaf
- Matte Leaf
- Wavy Leaf
- Curved Leaf
- Flat Leaf
- Pointed Leaf
- Serrated Leaf
- Split Leaf
- Folded Leaf
- Fleshy Leaf
- Spotted Leaf
- Veined Leaf
- Parallel Leaf
- Toothed Leaf
- Net Leaf
- Long Leaf
- Short Leaf
- Narrow Leaf
- Wide Leaf
Different Types of Leaves Names in English with Images
- Glossy Leaf
A leaf with a shiny, reflective surface caused by a waxy coating, helping reduce water loss, repel dust, and protect tissues while enhancing light reflection in bright growing conditions areas.

- Matte Leaf
A leaf with a dull, non-shiny surface that absorbs light evenly, often soft in appearance, reducing glare and supporting steady photosynthesis in shaded or moderately lit environments during plant growth.

- Wavy Leaf
A leaf whose edges form gentle waves instead of straight lines, giving flexibility, improved airflow, and a decorative look while maintaining normal photosynthesis and healthy growth in many plant species.

- Curved Leaf
A leaf that bends smoothly along its length or margins rather than lying straight, helping direct water runoff, adjust light exposure, and tolerate wind without tearing in natural outdoor conditions.

- Flat Leaf
A leaf with an even, level surface lacking folds or curves, allowing maximum sunlight capture, efficient gas exchange, and balanced growth in many common plant species across different habitats worldwide.

- Pointed Leaf
A leaf ending in a sharp or narrow tip, helping rainwater drip away quickly, reducing moisture buildup and lowering disease risk in humid growing environments for healthier plant survival overall.

- Serrated Leaf
A leaf with sharp, saw-like teeth along its edges, which may deter herbivores, increase edge area, and improve water drainage during rainfall in many wild and cultivated plant species worldwide.

- Split Leaf
A leaf whose blade has deep cuts or openings, not fully separated into leaflets, allowing better light penetration and air movement through large leaf surfaces in tropical climbing plant species.

- Folded Leaf
A leaf that is bent or folded along veins or the midrib, either naturally or temporarily, helping protect tissues and reduce water loss under stressful weather and environmental conditions outdoors.

- Fleshy Leaf
A leaf with thick, soft, water-storing tissues, adapted to dry climates, enabling plants to survive drought by conserving moisture for long periods without frequent rainfall or regular watering needs naturally.

- Spotted Leaf
A leaf showing visible spots or patches of different colors, caused by pigmentation or patterns, often adding ornamental beauty to decorative plants grown indoors and outdoors in gardens worldwide today.

- Veined Leaf
A leaf with clearly visible veins forming a support network, transporting water and nutrients while giving strength and shape to the leaf blade during normal plant growth and development stages.

- Parallel Leaf
A leaf with veins running side by side from base to tip, typical of grasses and monocots, providing strength and efficient internal transport across long, narrow leaf surfaces naturally occurring.

- Toothed Leaf
A leaf with small, rounded or blunt teeth along the margin, less sharp than serrated edges, helping manage water flow during rain in many herbs, shrubs, and garden plants worldwide.

- Net Leaf
A leaf with veins forming a branching, net-like pattern, common in dicot plants, allowing flexibility and efficient distribution of nutrients throughout the leaf surface during active growth periods naturally worldwide.

- Long Leaf
A leaf that is much longer than it is wide, common in grasses and lilies, helping bend with wind and capture sunlight efficiently without breaking, tearing, or damage to tissues.

- Short Leaf
A leaf with limited length and compact size, often found on shrubs or ground plants, reducing exposure to wind and water loss in open areas, dry climates, and harsh conditions.

- Narrow Leaf
A leaf with a small width compared to its length, adapted to windy or dry habitats, helping reduce surface area and moisture loss during hot, sunny, and exposed weather periods.

- Wide Leaf
A leaf with a broad blade that spreads outward, increasing sunlight absorption and photosynthesis, common in tropical and shade-loving plants growing under dense forest canopies or low-light garden conditions naturally.

Learn more helpful Articles