List of Metals with Names in English
- Iron
- Steel
- Copper
- Gold
- Silver
- Aluminum
- Tin
- Lead
- Zinc
- Nickel
- Titanium
- Chromium
- Platinum
- Palladium
- Bronze
- Brass
- Magnesium
- Cobalt
- Cadmium
- Tungsten
Different Types of Metals with Names and Pictures
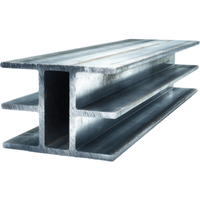
- Iron
A strong, widely used metal found in earth’s crust, essential for construction, machinery, and tools; it rusts when exposed to moisture unless protected or alloyed with other elements.

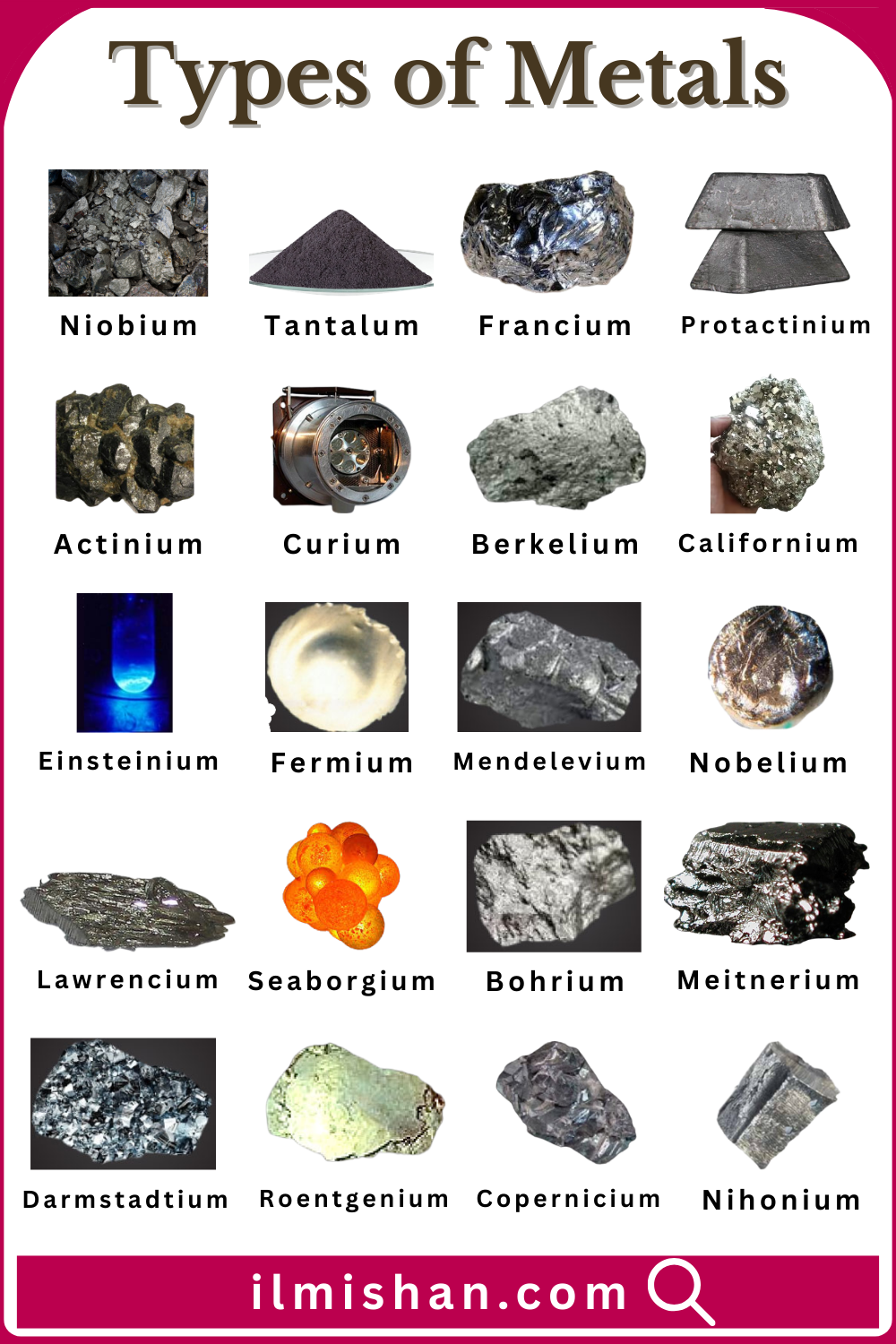
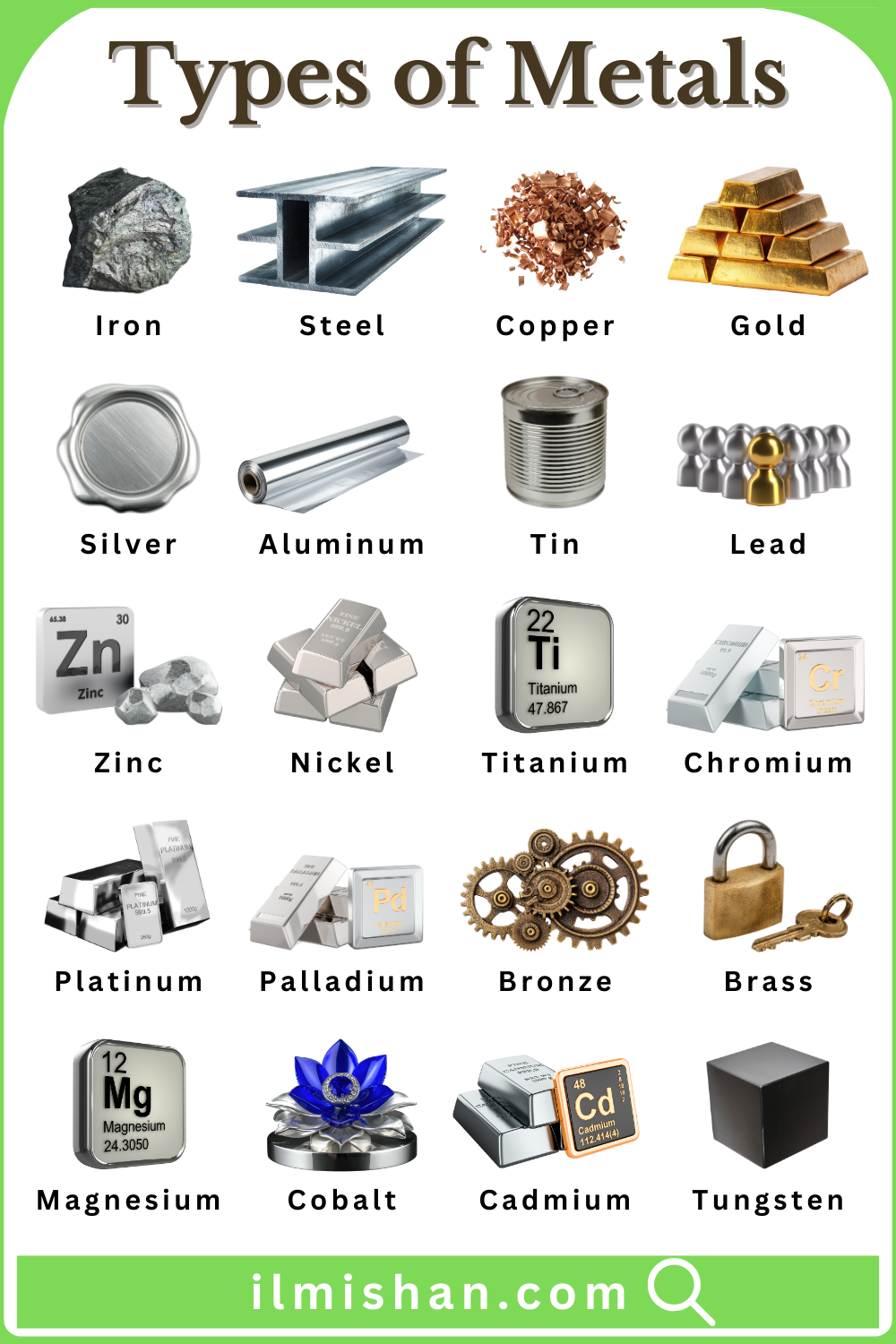
- Steel
A tough alloy made mainly from iron and carbon, used for buildings, bridges, vehicles, and tools because of its high strength, durability, and ability to be shaped or heat-treated.
- Copper
A reddish metal known for excellent electrical and heat conductivity, used in wires, plumbing, electronics, and alloys because it resists corrosion and is easy to shape and recycle.

- Gold
A soft, yellow, corrosion-free precious metal used in jewelry, electronics, dentistry, and investment due to its rarity, electrical conductivity, long-lasting shine, and resistance to chemical reactions.

- Silver
A shiny white precious metal with the highest electrical and thermal conductivity, commonly used in jewelry, mirrors, electronics, medical tools, and photography, though it tarnishes when exposed to sulfur.

- Aluminum
A lightweight, silver-gray metal that resists rust, used in airplanes, vehicles, cans, construction, and household items because it is strong, flexible, and easily recycled.

- Tin
A soft, silvery metal used mainly for coating steel to prevent rust and for soldering electronics, valued for its low melting point, corrosion resistance, and smooth bonding properties.

- Lead
A heavy, soft, bluish-gray metal used in batteries, radiation shielding, and industrial products; toxic to humans, requiring careful handling and strict safety controls during use.

- Zinc
A corrosion-resistant metal often used to coat iron and steel to stop rust, also used in brass, batteries, die-cast products, and as an important nutrient for plants and humans.

- Nickel
A hard, silver-white metal used to make stainless steel, batteries, coins, and corrosion-resistant coatings because it improves strength, hardness, and resistance to heat and oxidation.

- Titanium
A strong, lightweight metal known for excellent corrosion resistance, commonly used in aircraft, medical implants, and high-performance products due to its biocompatibility and exceptional strength-to-weight ratio.

- Chromium
A shiny, hard metal used to make stainless steel and chrome plating, providing corrosion resistance, hardness, and a reflective surface in tools, automotive parts, and decorative items.

- Platinum
A dense, silver-white precious metal resistant to corrosion, widely used in catalytic converters, jewelry, medical equipment, and chemical industries because of its stability and powerful catalytic properties.

- Palladium
A rare, silver-white metal used in catalytic converters, electronics, hydrogen storage, and jewelry due to its strong catalytic ability, corrosion resistance, and high value in industrial applications.

- Bronze
A durable alloy of copper and tin, historically used for weapons, tools, and art; valued today for strength, corrosion resistance, and suitability for sculptures, bearings, and mechanical parts.

- Brass
An alloy of copper and zinc known for bright gold-like appearance, corrosion resistance, and ease of shaping, used in instruments, fittings, valves, decorative pieces, and machine parts.

- Magnesium
A very light, silver-white metal used in aircraft parts, electronics, fireworks, and alloys because of its low weight, good strength, and essential role in biological processes.

- Cobalt
A hard, gray metal used in batteries, magnets, alloys, and jet engines due to its heat resistance, strength, and ability to stabilize rechargeable battery chemistry.

- Cadmium
A soft, bluish metal used in batteries, coatings, and pigments, known for corrosion resistance but highly toxic, requiring strict environmental and safety controls during production and handling.

- Tungsten
A very dense, extremely high-melting metal used in light bulb filaments, cutting tools, and heavy-duty machinery because of its exceptional hardness, heat resistance, and durability.

Metal with Name List In English
- Mercury
- Bismuth
- Lithium
- Sodium
- Potassium
- Calcium
- Strontium
- Barium
- Thorium
- Uranium
- Cesium
- Rubidium
- Gallium
- Indium
- Thallium
- Germanium
- Zirconium
- Hafnium
- Vanadium
- Manganese
Common Types of Metals with Names in English and Pictures
- Mercury
A heavy silver liquid metal at room temperature used in thermometers scientific instruments and some industrial processes but toxic and harmful to living organisms.

- Bismuth
A brittle pinkish white metal known for its low toxicity and used in medicines cosmetics alloys and fire safety devices due to its low melting point.

- Lithium
A very light soft metal used in rechargeable batteries electric vehicles and portable electronics because it stores energy efficiently and reacts easily.

- Sodium
A soft highly reactive metal that reacts strongly with water and is used in street lights heat transfer systems and chemical production.

- Potassium
A soft reactive metal essential for plant and human life and mainly used in fertilizers soaps and certain chemical manufacturing processes.

- Calcium
A reactive metal important for bones teeth and living cells and widely used in construction materials metal refining and chemical production.

- Strontium
A soft silvery metal used in fireworks to produce red color and in certain medical and industrial applications.

- Barium
A soft heavy metal used in medical imaging to view the digestive system and in drilling fluids paints and glass manufacturing.

- Thorium
A radioactive metal considered as a potential nuclear fuel and used in specialized alloys and high temperature scientific applications.

- Uranium
A heavy radioactive metal primarily used as fuel in nuclear power plants and in military applications due to its ability to produce energy through fission.

- Cesium
A very soft highly reactive metal used in atomic clocks drilling fluids and scientific research because of its precise frequency properties.

- Rubidium
A soft reactive metal used in research atomic clocks and special types of glass and electronic components.

- Gallium
A soft metal that melts near room temperature and used in semiconductors LEDs and solar panels for electronic devices.

- Indium
A soft silvery metal used in touch screens liquid crystal displays and low melting alloys in electronics manufacturing.

- Thallium
A soft heavy metal once used in pesticides and electronics but highly toxic and now limited to specialized scientific uses.

- Germanium
A hard gray metal like element used in semiconductors fiber optics and infrared optics for electronic and communication devices.

- Zirconium
A strong corrosion resistant metal used in nuclear reactors chemical processing equipment and high performance ceramics.

- Hafnium
A dense corrosion resistant metal used in nuclear control rods superalloys and advanced semiconductor technology.
- Vanadium
A strong gray metal added to steel to increase strength toughness and resistance to wear in tools vehicles and construction materials.

- Manganese
A hard brittle metal essential in steel production and used in batteries chemicals and to improve strength and durability of alloys.

20 Names of Metals in English
- Rhenium
- Osmium
- Iridium
- Ruthenium
- Rhodium
- Scandium
- Yttrium
- Lanthanum
- Cerium
- Neodymium
- Samarium
- Europium
- Gadolinium
- Terbium
- Dysprosium
- Holmium
- Erbium
- Thulium
- Ytterbium
- Lutetium
Most Popular Types of Metals with Names and Images
- Rhenium
A very dense and heat resistant metal used in jet engines and high temperature alloys to maintain strength under extreme heat and pressure.

- Osmium
One of the densest natural metals known for its hardness and durability and mainly used in special alloys and wear resistant applications.

- Iridium
A hard corrosion resistant platinum group metal used in spark plugs crucibles and equipment exposed to very high temperatures.

- Ruthenium
A rare platinum group metal used to strengthen alloys and widely applied in electronics and industrial chemical catalysts.

- Rhodium
A shiny silver white metal valued for corrosion resistance and commonly used in catalytic converters and jewelry plating.

- Scandium
A lightweight silvery metal added to aluminum alloys to increase strength while keeping materials light for aerospace and sports equipment.

- Yttrium
A soft silvery metal used in LED lights lasers and advanced ceramic materials for modern technology.

- Lanthanum
A soft reactive rare earth metal used in camera lenses battery electrodes and refining catalysts to improve performance.

- Cerium
A reactive rare earth metal used in glass polishing lighter flints and catalytic converters due to its chemical flexibility.

- Neodymium
A rare earth metal famous for producing very strong magnets used in motors headphones and wind turbines.

- Samarium
A rare earth metal used in powerful magnets nuclear reactor control rods and special heat resistant glass.

- Europium
A soft rare earth metal mainly used in red and blue phosphors for LED lights and display screens.

- Gadolinium
A silvery rare earth metal used in MRI contrast agents nuclear reactors and special magnetic materials.

- Terbium
A rare earth metal used in green phosphors for lighting and displays and added to magnets for better performance.

- Dysprosium
A rare earth metal added to strong magnets to improve heat resistance in electric vehicles and energy systems.

- Holmium
A rare earth metal known for strong magnetic properties and used in medical lasers and nuclear control rods.

- Erbium
A soft rare earth metal used in fiber optic cables and signal amplifiers to strengthen light signals.

- Thulium
One of the least abundant rare earth metals used in portable X ray machines and certain laser devices.

- Ytterbium
A soft rare earth metal used in lasers special alloys and atomic clocks for precise scientific applications.

- Lutetium
A dense rare earth metal used in PET scan detectors oil refining catalysts and advanced medical research.

All Types of Metal list in English
- Niobium
- Tantalum
- Francium
- Protactinium
- Actinium
- Curium
- Berkelium
- Californium
- Einsteinium
- Fermium
- Mendelevium
- Nobelium
- Lawrencium
- Seaborgium
- Bohrium
- Meitnerium
- Darmstadtium
- Roentgenium
- Copernicium
- Nihonium
Common Metals Types with their Pictures
- Niobium
A soft gray metal used mainly in steel alloys to increase strength without adding much weight and also used in superconducting magnets and special high temperature materials.

- Tantalum
A hard corrosion resistant metal used in electronic capacitors medical implants and chemical equipment because it can withstand heat and harsh environments.

- Francium
An extremely rare and highly radioactive metal that exists only in tiny amounts in nature and is mainly studied for scientific research.

- Protactinium
A dense radioactive metal found in uranium ores and mainly used for scientific study due to its scarcity and instability.

- Actinium
A highly radioactive metal that glows faintly in the dark and is used in research and certain targeted cancer treatments.

- Curium
A radioactive synthetic metal produced in nuclear reactors and used in scientific research and as a power source in some space missions.

- Berkelium
A radioactive synthetic metal created in laboratories and used mainly for scientific experiments and producing heavier elements.

- Californium
A highly radioactive metal used in neutron sources for nuclear reactors medical treatments and detecting materials in industry.

- Einsteinium
A synthetic radioactive metal produced in nuclear reactions and used only for scientific research because of its short half life.

- Fermium
A man made radioactive metal formed in nuclear explosions or reactors and studied only for advanced scientific research.
- Mendelevium
A synthetic radioactive metal produced in particle accelerators and used only for research on heavy elements.

- Nobelium
A radioactive synthetic metal created in laboratories and studied for understanding nuclear properties of heavy elements.

- Lawrencium
A synthetic radioactive metal that exists only in laboratories and is researched to study atomic structure and behavior of heavy elements.

- Seaborgium
A man made radioactive metal produced in particle accelerators and studied to explore properties of superheavy elements.

- Bohrium
A synthetic radioactive metal created in laboratories and researched for its short lived nuclear properties.

- Meitnerium
A highly unstable synthetic metal produced in particle accelerators and studied only for scientific investigation of superheavy elements.

- Darmstadtium
A radioactive synthetic metal created in laboratories and researched to understand chemical behavior of very heavy atoms.

- Roentgenium
A man made radioactive metal produced in particle accelerators and studied for its short lived atomic characteristics.

- Copernicium
A synthetic radioactive metal with very unstable atoms produced in laboratories and researched for advanced nuclear studies.

- Nihonium
A highly radioactive synthetic metal created in particle accelerators and studied to expand knowledge of superheavy chemical elements.

Learn more helpful articles